EN-ICHI Opens Up the Future of Family and Community
[Info. File] An Analysis of the “Comprehensive Measures for the Acceptance of Foreign Nationals and Orderly Coexistence” (January 23, 2026)

On January 23, 2026, under Prime Minister Takaichi, the Ministerial Meeting on the Acceptance of Foreign Nationals and Realization of a Society of Orderly Coexistence was convened. At the meeting, the “Comprehensive Measures for the Acceptance of Foreign Nationals and Orderly Coexistence” was formulated and released. These Comprehensive Measures set forth the core policies and guidelines through which the Government of Japan aims to realize a society in which foreign nationals and Japanese citizens live together in harmony.
The predecessor framework, the “Comprehensive Measures for Acceptance of Foreign Workers and Coexistence”, was first formulated in 2018 at the Ministerial Meeting on Acceptance of Foreign Workers and Coexistence and has been revised annually since then. Following the inauguration of the Takaichi administration in October 2025, a new post—Minister in Charge of Promoting a Society of Orderly Coexistence with Foreign Nationals—was established, along with the creation of the current Ministerial Meeting. This led to the formulation of the present Measures.
- What Has Changed?
- Basic Principles for Comprehensive Measures for the Acceptance of Foreign Nationals and Orderly Coexistence
- Direction of reform of various systems
- Optimization of Immigration and Residence Management and Promotion of DX
- Stricter Screening and Review of Statuses of Residence
- Strong Promotion of Measures Against Overstaying and Illegal Employment
- Optimization of the Tax, Social Security, and Medical Systems
- Appropriate Use and Management of National Land (Land Acquisition Rules)
- Improving Japanese Language Education and Framwork for Integration
- Numerical Targets and Future Outlook
- Conclusion
What Has Changed?
A comparison between the “Comprehensive Measures for Acceptance of Foreign Workers and Coexistence” (FY2025 Revised Edition) and the newly adopted “Comprehensive Measures for the Acceptance of Foreign Nationals and Orderly Coexistence” (January 2026) reveals a significant conceptual shift. As reflected in the title, the long-standing principle of coexistence has been strengthened by the explicit addition of order.
In response to public concerns and perceptions of unfairness arising from certain foreign nationals’ violations of laws and rules, or improper use of systems, the government now places greater emphasis on ensuring “public safety and peace of mind” and “compliance with rules” as the foundation of a society of orderly coexistence. While continuing existing coexistence initiatives, the new Measures represent a decisive shift toward closing institutional loopholes and strengthening enforcement to ensure that “those who abide by the rules are properly recognized.”
At the same time, progress has been made in improving the framework of integration, including consideration of nationally led programs for learning the Japanese language and Japan’s systems and rules. New policy areas have also been added, including: Appropriate use and management of national land, Countermeasures against private lodging (minpaku) and overtourism and Initial educational support for children of foreign nationals.
Basic Principles for Comprehensive Measures for the Acceptance of Foreign Nationals and Orderly Coexistence
The key points of the “Basic Principles” presented at the beginning of the Measures are summarized below (Figure 1).
Figure 1: key points of the “Basic Principles”
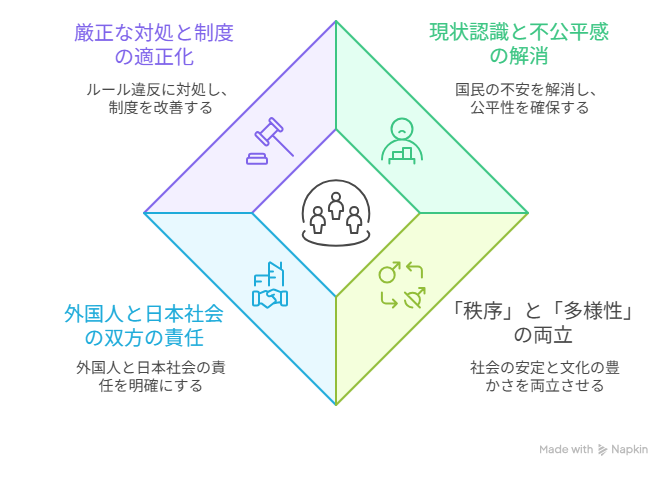
Source: Compiled by the author
1. Addressing Public Anxiety and Perceived Unfairness
As the number of foreign residents reaches a record high, the government recognizes the need to appropriately respond to violations of laws and improper system use, and to resolve public concerns and perceptions of unfairness.
2. Balancing “Order” and “Diversity”
Order is positioned as the foundation of society, and diversity as its strength. The aim is to build a society in which foreign nationals who comply with the rules are properly evaluated and can live with dignity.
3. Clarifying Responsibilities on Both Sides
Foreign nationals are expected to begin studying the Japanese language prior to entry, to learn about Japan’s social norms and institutional systems, and to act responsibly as members of their local communities.
Japanese society bears the responsibility of establishing and fairly operating clear rules, making those rules linguistically accessible and visible, and developing an appropriate framework of integration under national responsibility. This includes close coordination with local governments, as well as clarifying the roles and responsibilities of receiving organizations, such as companies and other institutions.
4. Strict Enforcement and Institutional Reform
Violations of rules will be addressed strictly regardless of nationality. Existing systems—many of which were not designed for large foreign resident populations—will be improved to reflect current realities.
As of the end of June 2025, the number of foreign residents in Japan reached approximately 3.96 million, continuing to set new records. In light of this growth and associated public concerns, the government positions “order” as the foundation of society and commits to fundamental institutional reforms.
Direction of Institutional Reforms
Reforms toward a society of orderly coexistence are promoted from four main perspectives (Figure 2).
Figure 2 Pillars of institutional reform
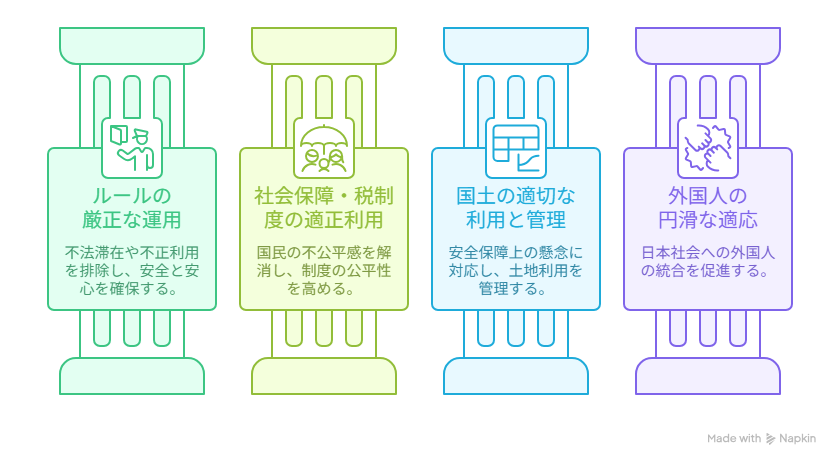
Source: Compiled by the author
1. Strict Enforcement and Optimization of Rules (Ensuring Safety and Peace of Mind)
The government will accelerate the digital transformation (DX) of immigration and residence management. Through measures such as integration with the My Number Card and the introduction of the Japan Electronic System for Travel Authorization (JESTA), it will thoroughly eliminate overstaying and improper use of systems.
2. Proper Use of Social Security and Tax Systems
In order to address public perceptions of unfairness, various systems will be optimized. This includes electronically verifying the payment status of insurance premiums and strengthening entry restrictions on individuals with unpaid medical expenses.
3.Appropriate Use and Management of National Land
To respond to national security concerns, the government will strengthen the identification of the nationality of land acquirers and formulate, by the summer of 2026, the basic framework for new legal rules governing land acquisition.
4. Measures to Facilitate Smooth Adaptation of Foreign Nationals to Japanese Society
The government will enhance Japanese language education for all generations and further develop the framework of integration so that foreign nationals can live more smoothly and stably in Japan.
Next, we will introduce in greater detail the main policy measures outlined in these Comprehensive Measures.
Optimization of Immigration and Residence Management and Promotion of DX
Digital technologies will be leveraged to achieve both faster screening and stricter management.
Advanced Immigration Control
Introduction of JESTA (Japan Electronic System for Travel Authorization)
With the aim of introducing the system within fiscal year 2028, it will prevent the entry into Japan of individuals intending to overstay before they arrive. In addition, entry and exit information for short-term visitors will be centrally managed.
Joint Kiosks and Walk-Through Gates
The government will promote the digitalization of customs and immigration procedures in order to achieve screening that is both rigorous and smooth.
Digital Transformation of Residence Management and Utilization of the My Number System
Strengthening Information Linkage
From March 2027 onward, the Immigration Services Agency of Japan will make use of the Public Service Mesh to directly obtain information from relevant institutions regarding local taxes, social insurance premiums, medical insurance, and other related data. This will enable the omission of certain supporting documents in residence procedures and allow for rigorous residence examinations in cases where unpaid obligations are identified.
Principle of Integrating the Residence Card and the My Number Card
The operation of the “Specified Residence Card, etc.” will commence in June 2026. In the future, the government aims for all mid- to long-term foreign residents to obtain this integrated card as a general rule.
Stricter Screening and Review of Statuses of Residence
As shown in Table 1, monitoring and enforcement measures will be strengthened against uses of statuses of residence that deviate from their intended purpose, as well as against particularly malicious cases.
Table 1: Major revisions and strengthening measures for each status of residence
| Status of residence | Major revisions and strengthening measures |
| Permanent Resident | Stricter review of compliance with public obligations (tax and insurance payments); addition of revocation grounds for willful nonpayment (effective April 2027). |
| Naturalization | Stricter review aligned with permanent residence standards; in principle requires ten years of residence. |
| Business Manager | Enhanced on-site investigations, particularly where small offices cluster in a single building. |
| Engineer/Specialist in Humanities/International Services | Strengthened monitoring of dispatched work; strict guidance for receiving organizations assigning non-qualifying tasks. |
| Student | Use of My Number income data to investigate violations of the 28-hour work limit. |
| Specified Skilled Worker / Employment for Skill Development | Launch of the new Employment for Skill Development system in FY2027; phased relaxation of job-change restrictions and improvement of Japanese language ability. |
Source: Compiled by the author
Strong Promotion of Measures Against Overstaying and Illegal Employment
Under the “Zero Overstayers Plan,” enforcement against violations of laws and regulations will be strengthened.
Promotion of Deportation
Following the enforcement of the 2023 amendment to the Immigration Control and Refugee Recognition Act, exceptions to the effect of suspension of deportation will be applied in order to ensure the prompt removal of individuals who have committed serious crimes and other significant violations. In addition, the number of government-funded deportations accompanied by escort officers will be doubled by 2027.
Measures Against Illegal Employment
The government will promote the widespread use of the Residence Card Reader App to prevent the use of forged residence cards.
Joint crackdowns by relevant ministries and agencies will be conducted against so-called “improper yards,” which are regarded as breeding grounds for illegal employment.
Furthermore, strict compliance with the obligation to submit notifications regarding the employment status of foreign nationals will be enforced, and penalties will be applied in cases of non-submission or false reporting.
Response to Crime
Interpreter services will be expanded, including enhanced information-sharing among prefectural police departments coordinated by the National Police Agency. Measures will also be strengthened to address crimes committed through the misuse of social networking services (SNS), including fraudulent and other improper activities.
Optimization of the Tax, Social Security, and Medical Systems
Measures will be implemented to eliminate perceptions of unfairness vis-à-vis Japanese citizens and to ensure the sustainability of the system.
National Health Insurance Premiums
Beginning in fiscal year 2026, foreign nationals will be permitted to make advance premium payments on a rolling basis during their first year after entry into Japan.
From June 2027 onward, payment information will be electronically verified for all statuses of residence and utilized in residence screening procedures.
Measures to Address Unpaid Medical Expenses
The threshold for stricter entry screening of foreign visitors with unpaid medical expenses will be lowered from the current minimum of ¥200,000 to ¥10,000.
The scope of these measures will also be expanded to include mid- to long-term residents, and the relevant information will be used in residence examinations.
In addition, institutional measures requiring enrollment in private medical insurance prior to entry into Japan will be considered.
Lump-Sum Childbirth and Childcare Allowance and Overseas Medical Expenses
To prevent fraudulent receipt of benefits, strict enforcement of the domestic residency requirement will continue, and screening procedures will be further strengthened.
Tax Treaties
Negotiations will be promoted to appropriately revise provisions in tax treaties that exempt the salaries of foreign students and others from taxation, in order to align them with international standards.
Appropriate Use and Management of National Land (Land Acquisition Rules)
Opacity in land ownership information will be eliminated in order to address national security risks.
Enhancing Transparency
Strengthening Identification of Nationality
The government will identify the nationality and beneficial ownership of landholders in real estate registries, agricultural land ledgers, and forest land ledgers, with phased implementation beginning in 2026.
In addition, amendments to the Foreign Exchange and Foreign Trade Act will expand reporting requirements to include real estate acquisitions
Countermeasures Concerning Groundwater and Condominiums
Understanding the Actual Conditions of Groundwater Extraction
By summer 2026, a unified framework—including nationality information—will be established to ascertain the actual conditions of groundwater extraction by foreign nationals and others.
Curbing Condominium Speculation
Measures will be taken to restrain short-term resales and speculative transactions that lack genuine residential demand. The government will follow up on initiatives such as imposing limits on the number of units that may be purchased, in coordination with the real estate industry.
New Rules from a National Security Perspective
Consideration of Legal Frameworkse
By summer 2026, the government will formulate the framework for new legal rules that would enable prior regulation of land acquisition from a national security perspective. These rules will extend beyond areas surrounding critical facilities and will be designed to balance national security considerations with the freedom of economic activity.
Improving Japanese Language Education and Framwork for Integration
The educational foundation necessary for foreign nationals to adapt to Japanese society and understand its rules will be strengthened.
Improving the Framework of Integration
Explanatory videos (available in 17 languages) outlining Japanese rules, manners, and institutional systems will be widely disseminated.
The promotion of “Easy Japanese” will be advanced in order to improve the clarity and accuracy of administrative information provided to foreign residents.
In addition, programs will be established for both prospective entrants and resident foreign nationals to learn the Japanese language as well as Japan’s social systems and rules.
Strengthening Japanese Language Education
- Before entry into Japan, support programs aimed at introducing and promoting Japanese language education overseas will be strengthened.
- For workers, model curricula for Japanese language instruction under the Employment for Skill Development system will be developed and widely disseminated.
- For foreign residents in daily life, online Japanese language learning materials will be expanded, and financial support for community-based Japanese language education will be enhanced.
- For children, support will be expanded for “Preschools” (provisional name) that provide initial assistance, as well as for Japanese language teaching assistants and related personnel.
Life-Stage-Specific Support
- For infants and school-age children, efforts will be made to eliminate cases of non-attendance at school.
- For youth in the early stages of adulthood, examples of schools organizing and implementing “Special Educational Curricula” for Japanese language instruction will be widely disseminated and promoted.
- For young adults, measures will be taken to promote the employment and active participation of international students. In addition, the dissemination and utilization of video materials and guidance promoting mutual learning between Japanese and foreign employees in the workplace will be encouraged.
- For older persons, continued and enhanced public outreach and information dissemination regarding the pension system will be considered.
Numerical Targets and Future Outlook
Finally, the numerical targets and implementation schedules for the principal measures are summarized in Table 2.
Table 2: Numerical Targets and Implementation Schedule for Major Measures

Source: Compiled by the author
Conclusion
As stated in these Comprehensive Measures, the circumstances surrounding the realization of a society of orderly coexistence with foreign nationals are expected to continue evolving. The process of building such a society is, in essence, the process of shaping the future form of Japanese society itself. It requires the proactive engagement of the national government, local governments, private companies and organizations, foreign residents, and Japanese citizens alike, who must continue to engage in dialogue and accumulate ongoing deliberation and decisive action.
References
- Ministerial Conference on the Acceptance and Coexistence of Foreign Workers (2025), “Comprehensive Measures for the Acceptance and Coexistence of Foreign Workers (Revised in 2025),” https://www.moj.go.jp/isa/content/001440747.pdf (last accessed January 30, 2026)
- Ministerial Conference on Acceptance of Foreign Nationals and the Realization of an Orderly Coexistence Society (2026), “Comprehensive Measures for Acceptance of Foreign Nationals and the Realization of an Orderly Coexistence Society,” https://www.kantei.go.jp/jp/singi/gaikokujinzai/pdf/kettei_honbun.pdf (last accessed February 5, 2026)
- Ministerial Conference on Acceptance of Foreign Nationals and the Realization of an Orderly and Cohesive Society (2026), “Outline of Initiatives for the Safety and Security of the People,” https://www.kantei.go.jp/jp/singi/gaikokujinzai/pdf/kettei_torikumi_gaiyo.pdf (last accessed February 5, 2026)
